Understanding Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Supraventricular Tachycardia, often abbreviated as SVT, is a fast heart rhythm that originates above the ventricles in the atria or AV node part of the heart. This condition may be scary, especially for athletes, who rely heavily on their cardiovascular health for optimal performance. However, SVT is typically not life-threatening, though it can cause significant discomfort and worry. Understanding SVT, its causes, and its impacts on the heart is the first step toward managing and overcoming this condition.
Why Athletes are at Risk of SVT
Athletes, particularly those involved in strenuous physical activities, are at an increased risk of SVT. The high levels of physical stress and exertion can cause the heart to work harder, potentially triggering this rapid heart rhythm. Additionally, certain dietary habits common among athletes, such as consuming high levels of caffeine or energy drinks, can also contribute to developing SVT.
Recognizing the Symptoms of SVT in Athletes
Recognizing the symptoms of SVT is crucial for early detection and treatment. Symptoms may include a sudden rapid heart rate, palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, or fainting. However, it's important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other conditions, so a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is essential.
How SVT is Diagnosed in Athletes
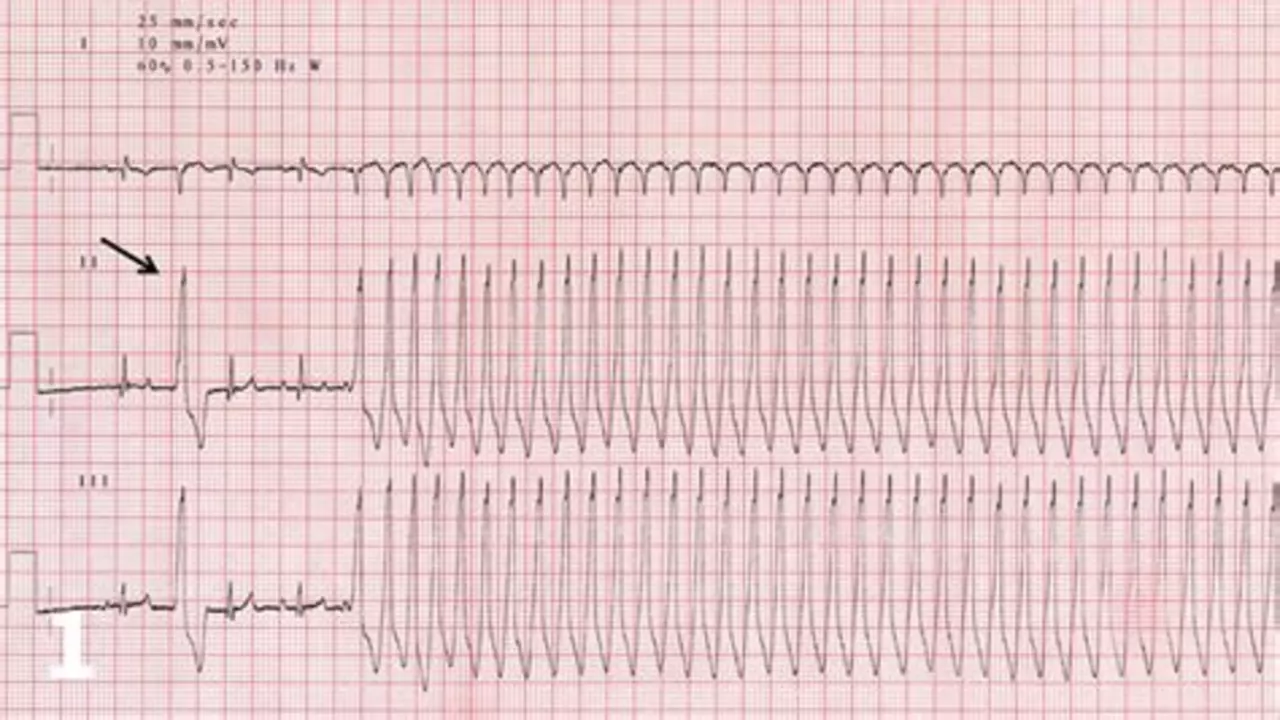
Diagnosing SVT in athletes involves a thorough examination and a series of tests. These may include an electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor the heart's electrical activity, a stress test to observe the heart under physical stress, and blood tests to check for underlying conditions. Your doctor may also ask about your symptoms and medical history to help make a diagnosis.
Managing SVT During Athletic Activities
Managing SVT during athletic activities can be challenging but is not impossible. It involves regular monitoring of your heart rate, taking prescribed medications as directed, and making lifestyle changes as needed. This might include reducing caffeine intake, ensuring adequate hydration, and adjusting training intensity. It's also essential to understand your body and know when to slow down or stop if symptoms occur.
Treatment Options for Athletes with SVT
Several treatment options are available for athletes with SVT. These may include medications to regulate the heart rate, cardioversion therapy to restore a normal heart rhythm, or ablation therapy to target the area of the heart causing the abnormal rhythm. The best treatment option will depend on the severity of your condition, your overall health, and your athletic goals.
The Impact of SVT on Athletic Performance
SVT can impact athletic performance in several ways. The most immediate effect is often a decrease in performance due to symptoms like dizziness or shortness of breath. However, with proper management and treatment, many athletes can continue to train and compete effectively. It's important to communicate with your healthcare provider and athletic trainer to ensure a safe and effective training plan.
Preventing SVT in Athletes
While not all cases of SVT can be prevented, there are steps athletes can take to reduce their risk. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, staying well-hydrated, and managing stress levels. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help detect any potential heart issues early.
The Role of Coaches and Trainers in Managing SVT
Coaches and trainers play a crucial role in managing SVT in athletes. They can help monitor symptoms, adjust training plans to accommodate the athlete's condition, and provide support and guidance. It's important for coaches and trainers to be knowledgeable about SVT and to work closely with healthcare providers to ensure the athlete's safety and well-being.






14 Comments
For athletes confronting supraventricular tachycardia, a structured approach is paramount. Begin by acquiring a comprehensive cardiac evaluation, including baseline ECG and stress testing, to delineate the specific arrhythmic pattern. Subsequent management should integrate evidence‑based pharmacotherapy, such as beta‑blockers, while monitoring for adverse effects. Complementary lifestyle modifications-moderating caffeine intake, ensuring optimal hydration, and implementing graduated training regimens-further attenuate episode frequency. Ultimately, adherence to a disciplined medical and conditioning plan will enable sustained performance without compromising cardiovascular health.
/p>Hey guys great info keep it simple stay hydrated and cut back on energy drinks you’ll feel better fast
/p>Let us marvel at the sheer audacity of the fitness industry, which so cavalierly peddles caffeine‑laden elixirs while conveniently ignoring the arrhythmic nightmares they may unleash.
/p>SVT, that delightfully rapid electrical misfire, is practically a badge of honor for anyone who mistakes a racing heart for a sign of superior endurance.
Athletes, with their insatiable appetite for VO2 max gains, apparently believe that the heart is an infinite rubber band that can be stretched beyond any physiological limit.
The article kindly points out that stress testing can expose these hidden glitches, yet the same trainers who prescribe marathon‑level intervals rarely schedule a simple nose‑bleed check.
One would think that a physician’s recommendation to curb energy drink consumption would be a no‑brainer, but apparently the neon‑colored cans wield a hypnotic power over the gym‑dwelling masses.
Meanwhile, the suggested pharmacologic interventions, such as beta‑blockers, are dismissed by the die‑hard cardio‑aficionados as the ultimate betrayal of “natural” performance.
What’s more, the notion of ablation therapy is treated like a secret society ritual, whispered about in hushed tones yet never seriously considered by the self‑proclaimed “hard‑core” crowd.
The article’s emphasis on hydration is commendable, though it seems to clash with the prevailing dogma that sweating profusely is the only true indicator of a good workout.
Let us not forget the role of coaches, those benevolent overseers who, despite their lofty titles, often possess the anatomical knowledge of a dishwasher.
When an athlete faints mid‑sprint, the immediate reaction is to attribute it to “just a bad day,” rather than to investigate the underlying tachyarrhythmia.
Consequently, the cascade of missed diagnoses continues, bolstering the myth that a racing heart is merely a sign of enthusiasm rather than a medical red flag.
The proposed preventive measures-moderating caffeine, managing stress, and regular check‑ups-are as revolutionary as suggesting that one should wear shoes while running.
Yet, the reception of such advice is often met with eye‑rolls, as if the suggestion were a personal affront to the athlete’s machismo.
In the grand tapestry of sports medicine, SVT is the unwanted thread that threatens to unravel the whole picture, demanding both respect and strategic intervention.
Therefore, until the culture of glorified overexertion evolves, we shall remain stuck in a perpetual loop of hype, ignorance, and avoidable heart palpitations.
Feel the rhythm, then pause.
/p>From a philosophical standpoint, the heart’s rapid cadence can be seen as a metaphor for the pace of modern ambition. When we push ourselves beyond natural limits, the body issues subtle warnings that merit contemplation rather than dismissal. Incorporating mindfulness practices-such as paced breathing and reflective journaling-can help athletes attune to these internal signals. Ultimately, recognizing the narrative our bodies tell us may lead to a more harmonious balance between performance and well‑being.
/p>Oh sure, just ignore the pounding heart and sprint like a caffeinated squirrel; what could possibly go wrong? The elegance of “I’m fine” masks a ticking time‑bomb that most coaches pretend not to see. If you enjoy flirting with danger for the sake of a fleeting podium, then by all means keep treating your heart like a disposable battery.
/p>As a seasoned practitioner, I recommend starting with a thorough electrophysiology study to pinpoint the SVT focus. If medication is chosen, choose a rate‑controlling beta‑blocker and monitor response over a few weeks. Lifestyle tweaks-cutting coffee, staying hydrated, and avoiding extreme heat-often reduce episode frequency dramatically. In refractory cases, catheter ablation offers a curative option with high success rates. Always keep an open line with your sports physician to tailor the plan to your training schedule.
/p>The claim that energy drinks are the main culprit is overblown. Most athletes have underlying predispositions that make SVT more likely, regardless of caffeine. Focus on comprehensive cardiac screening rather than vilifying a single substance.
/p>Honestly, if you’re not already monitoring your heart with a smartwatch, you’re practically asking for trouble. Those “professional” training programs often skip the basics-like checking resting heart rate variability-while preaching elite performance. It would serve you well to demand a full arrhythmia workup before signing any new contract.
/p>Let’s light this up! Picture your heart as a high‑octane engine that sometimes revs a little too hard-SVT is just the turbo kicking in at the wrong moment. The good news? You can dial it back with smart training cycles, tech‑driven heart‑rate zones, and a splash of zen. Think of ablation as swapping out a misbehaving spark plug for a flawless one. Keep the fire, just make sure it doesn’t scorch the stadium!
/p>It’s fascinating how the autonomic nervous system can flip a switch and send the atria into overdrive during intense bouts. Recent studies show that structured cooldowns and progressive overload can modulate this response effectively. Integrating interval training with consistent heart‑rate monitoring provides actionable data to preempt episodes. Staying ahead of the curve means treating the heart as a partner, not a mere instrument.
/p>yo guys its real simple stay hydrated dont overdo the coffee and listen to your bodi when it says slow down
/p>In the grand theatre of athletic endeavour, the heart assumes a role both noble and precarious. When supraventricular tachycardia entrances the stage, it conducts a tumultuous overture that can unbalance even the most disciplined performer. Thus, a judicious blend of medical oversight and disciplined regimen becomes indispensable, lest the curtain fall prematurely upon a promising career. The physician, akin to a seasoned director, must orchestrate pharmacologic interludes and, where warranted, procedural intermissions with precision. Only through such harmonious collaboration can the athlete reclaim the symphony of rhythmic stability. Let us, therefore, champion vigilance and compassion as the pillars upon which lasting athletic excellence rests.
/p>Honestly, if you think a racing heart is just “excitement,” you’re living in a fantasy 😂. Real athletes respect the warning signs and act before the drama hits the fan. Stay smart, stay alive! 🌟
/p>