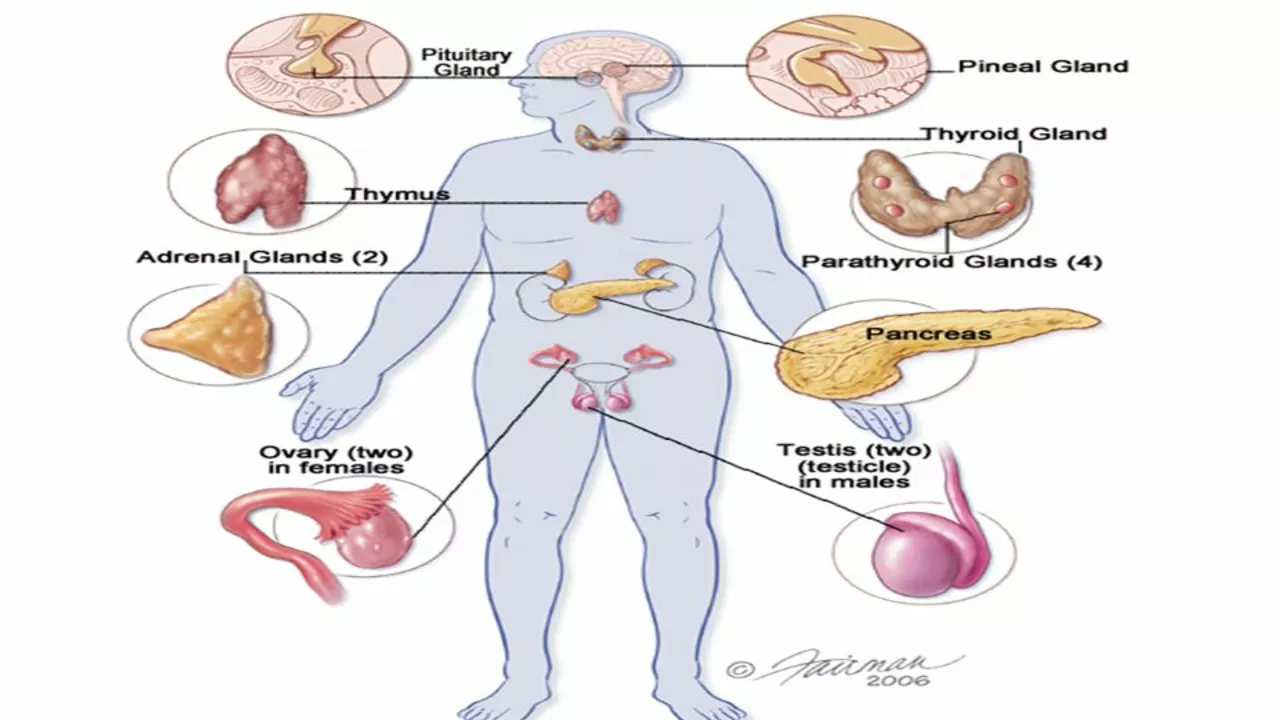
Understanding Hyperprolactinaemia and Hormonal Imbalance
In this section, we'll dive into the basics of hyperprolactinaemia and how it can lead to a hormonal imbalance in the body. Hyperprolactinaemia is a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. Prolactin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in milk production, as well as in the regulation of the menstrual cycle and fertility. When there is an excess of prolactin in the system, it can lead to a hormonal imbalance, causing a range of symptoms and health issues.
It's important to understand the role of hormones in our bodies because they act as chemical messengers, controlling and regulating various bodily functions. When there's an imbalance in our hormone levels, it can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being. In the case of hyperprolactinaemia, the excess prolactin can interfere with the normal functioning of other hormones, leading to a wide range of symptoms and complications.
Identifying the Symptoms of Hyperprolactinaemia
Hyperprolactinaemia can present with various symptoms, depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. Some of the most common signs of hyperprolactinaemia include irregular menstrual periods or the absence of periods altogether, unexplained weight gain, decreased libido, and infertility. Additionally, women with hyperprolactinaemia may experience galactorrhea, or the production of breast milk outside of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Men can also suffer from hyperprolactinaemia, and their symptoms may include erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissue. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other health issues, so it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hyperprolactinaemia
There are several potential causes of hyperprolactinaemia, ranging from underlying medical conditions to certain medications. Some of the most common causes include pituitary tumors, hypothyroidism, kidney and liver dysfunction, and certain medications such as antipsychotics and antidepressants. Additionally, stress and pregnancy can also lead to increased prolactin levels, but these are usually temporary and resolve once the stressor or pregnancy is over.
Understanding the potential risk factors for hyperprolactinaemia can help with early detection and treatment. Some factors that may increase an individual's risk of developing this condition include a family history of pituitary tumors, certain autoimmune disorders, and exposure to radiation in the head and neck area.
Diagnosing Hyperprolactinaemia
If you suspect that you may be suffering from hyperprolactinaemia, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis. The diagnostic process typically involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure prolactin levels. In some cases, additional tests may be required, such as thyroid function tests, kidney and liver function tests, and imaging studies like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to identify any potential pituitary tumors.
It is crucial to obtain an accurate diagnosis so that appropriate treatment can be initiated and any underlying causes can be addressed.
Treatment Options for Hyperprolactinaemia
Once hyperprolactinaemia has been diagnosed, the treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. In some cases, adjusting or discontinuing certain medications that contribute to increased prolactin levels may be sufficient to resolve the issue. If a pituitary tumor is the cause, treatment options may include medications to shrink the tumor, radiation therapy, or surgery.
For individuals with hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone replacement therapy can help normalize prolactin levels. In some cases, lifestyle changes may also be recommended, such as stress management techniques, to help address the hormonal imbalance. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and concerns.
Managing the Effects of Hormonal Imbalance
Living with a hormonal imbalance can be challenging, but there are several strategies that can help manage the symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can go a long way in supporting overall hormonal balance and well-being.
Additionally, stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce the impact of stress on hormone levels. It is also important to stay informed about your condition and work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure that your treatment plan is tailored to your needs and that any necessary adjustments are made promptly.
Conclusion
Hyperprolactinaemia is a complex condition that can lead to hormonal imbalances and a range of associated symptoms and health issues. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing this condition and minimizing its impact on an individual's quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for hyperprolactinaemia, you can take an active role in managing your hormonal health and well-being.




9 Comments
Contemplating the intricate feedback loops of the endocrine system reveals how hyperprolactinaemia can perturb homeostasis. Elevated prolactin does not operate in isolation; it modulates dopaminergic inhibition and interacts with gonadotropin-releasing hormone pathways. Consequently, menstrual irregularities and diminished libido emerge as logical sequelae. Moreover, the pituitary axis may experience mass effect when adenomas secrete excess prolactin. Recognizing these mechanistic underpinnings aids clinicians in differentiating primary prolactin excess from secondary hormonal disturbances.
/p>Understanding the ripple effect of high prolactin can really empower you to take charge of your health. First, track any menstrual changes or unexpected milk production – they’re often the earliest clues. Second, discuss medication reviews with your doctor; some prescriptions silently raise prolactin levels. Finally, incorporating stress‑relief practices like short walks or breathing exercises can help keep hormone levels steadier. Small, consistent steps often lead to big improvements over time.
/p>Balancing the physiological narrative with personal experience can ease anxiety surrounding the diagnosis. While laboratory values provide objective data, individual symptom patterns guide nuanced treatment choices. Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures adjustments are timely and effective.
/p>Hey folks, just wanted to add that lifestyle tweaks matter a lot when dealing with hormonal hiccups. Regular exercise, especially strength training, can boost natural testosterone and improve overall hormone balance. Also, keep an eye on your diet – plenty of leafy greens and lean proteins support pituitary health. If you feel down, a quick chat with a supportive friend can lift your mood more than you think. Stay positive and keep moving forward!
/p>Wow, nobody told me I’d need a PhD to understand my own body… 🙄
/p>From a pathophysiological perspective, hyperprolactinaemia constitutes a paradigmatic example of endocrine dysregulation wherein hypersecretion of lactotroph-derived prolactin engenders a cascade of downstream perturbations across the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑gonadal (HPG) axis, the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑thyroid (HPT) axis, and the broader neuroendocrine milieu. Elevated circulating prolactin exerts inhibitory control over dopaminergic tone via the tuberoinfundibular pathway, thereby attenuating the pulsatile release of gonadotropin‑releasing hormone (GnRH) and precipitating a clinical phenotype characterized by anovulation, amenorrhea, and diminished androgenic drive. Concurrently, prolactin-mediated upregulation of corticotropin‑releasing hormone (CRH) can potentiate adrenal cortisol output, further contributing to metabolic derangements such as insulin resistance and central adiposity. The etiological heterogeneity of hyperprolactinaemia-ranging from macroadenomatous prolactinomas to iatrogenic induction by dopamine antagonist pharmacotherapy-necessitates a stratified diagnostic algorithm incorporating quantitative immunoassays, magnetic resonance imaging of the sellar region, and comprehensive assessment of coexistent endocrine disorders, notably hypothyroidism, which can amplify prolactin synthesis via thyrotropin‑releasing hormone (TRH) cross‑stimulation. Therapeutic interventions should be individualized, with dopamine agonists such as cabergoline representing first‑line pharmacotherapy due to their high affinity for D2 receptors and favorable side‑effect profile, while surgical resection remains reserved for refractory or compressive macroadenomas. Adjunctive measures, including lifestyle optimization-regular aerobic activity, micronutrient‑rich diets, and stress mitigation techniques-serve to modulate neuroendocrine feedback loops and augment pharmacologic efficacy. Longitudinal monitoring of serum prolactin concentrations, tumor dimensions, and reproductive function is imperative to ensure sustained remission and to preempt potential complications such as optic chiasm compression or osteopenia secondary to chronic hypogonadism. In sum, a multidimensional approach encompassing precise etiological delineation, targeted pharmacotherapy, surgical consideration, and holistic lifestyle modification constitutes the cornerstone of effective management of hyperprolactinaemia and its attendant hormonal imbalances.
/p>The preceding exposition is thorough, yet a few grammatical refinements merit attention. Replace “hypersecretion” with “hyper‑secretion” for consistency, and consider hyphenating “dopamine‑antagonist” when referring to pharmacologic agents. Additionally, the phrase “macroadenatous prolactinomas” appears to contain a typographical error; the correct term is “macroadenomatous”. Finally, ensure parallel structure in the list of axes by formatting “hypothalamic‑pituitary‑gonadal (HPG) axis, the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑thyroid (HPT) axis, and the broader neuroendocrine milieu” consistently. Minor edits enhance readability without altering the substantive content.
/p>What an uplifting reminder that even complex hormonal challenges can be tackled with optimism! Embracing a proactive mindset not only fuels adherence to treatment plans but also amplifies the body’s intrinsic healing capacities. By celebrating small victories-like a restored menstrual cycle or a boost in energy-you reinforce positive neurochemical loops that sustain motivation. Let’s keep championing each other, sharing success stories, and turning setbacks into stepping stones toward vibrant health. Together we rise, stronger than any endocrine hurdle!
/p>While your rose‑colored glass is admirable, let’s not ignore the gritty reality that many patients wrestle with insurance roadblocks and medication side‑effects that no amount of optimism can magically erase. The dramatics of “stepping stones” feel a tad disconnected from the day‑to‑day slog of blood draws, MRI appointments, and the palpable anxiety of tumor monitoring. A more grounded narrative would acknowledge both the triumphs and the tribulations without glossing over the systemic obstacles that often dictate outcomes. That said, your enthusiasm is commendable, just remember to anchor it in pragmatic counsel.
/p>